2021-04-23

In order to select bearings, many factors need to be analyzed and studied and evaluated from various angles. There is no special specification for the selection procedure of bearings, but the general order is as follows:
(1) Master the mechanical device and the use conditions of the bearing, etc. (2) make clear the requirements for the bearing (3) select the type of bearing (4) select the bearing configuration (5) select the bearing size (6) select the bearing specification.
01 bearing load
Load size load size is usually the decisive factor in the selection of bearing size. The bearing capacity of roller bearing is larger than that of ball bearing with the same dimension. Generally, ball bearing is suitable for light or medium load, roller bearing is suitable for bearing heavy load.
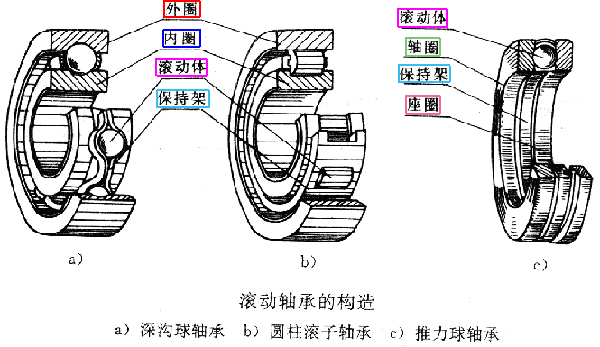
Load mode pure radial load can choose deep groove ball bearing, cylindrical roller bearing. Pure axial load can choose thrust ball bearing, thrust cylindrical roller bearing. When there is radial load and axial load (combined load), angular contact ball bearing or tapered roller bearing is generally selected. If the radial load is large and the axial load is small, deep groove ball bearing and cylindrical roller bearing with rib in inner and outer ring can be selected. In case of large deformation of shaft or shell and poor alignment, self-aligning ball bearing and self-aligning roller bearing can be selected. If the axial load is large and the radial load is small, the thrust angular contact ball bearing can be selected. If the four point contact ball bearing also requires the self-aligning performance, the thrust self-aligning roller bearing can be selected.
02 rotation accuracy
For most machines, the bearing with grade 0 tolerance is enough to meet the requirements of the host machine, but when there are strict requirements for the rotation accuracy of the shaft, such as machine tool spindle, precision machinery and instruments, the deep groove ball bearing, angular contact ball bearing, tapered roller bearing, cylindrical roller bearing and thrust angular contact ball bearing with higher tolerance grade should be selected.
03 noise and vibration
The noise and vibration of the bearing itself are generally very low. But for small and medium-sized motors, office machinery, household appliances and instruments, which have special requirements for noise and running stability, low-noise bearings are usually used.
04 rigidity
The rigidity of rolling bearing is determined by its elastic deformation under load. Generally, the deformation is very small and can be ignored. But in some machines, such as machine tool spindle system, the static stiffness and dynamic stiffness of bearing have a great influence on the characteristics of the system. Roller bearing has higher stiffness than ball bearing. The rigidity of all kinds of bearings can also be improved by proper "pre tightening".
05 speed
The working speed of rolling bearing mainly depends on its allowable operating temperature. The bearing with low friction resistance and less internal heating is suitable for high-speed operation. When only bearing radial load, deep groove ball bearing and cylindrical roller bearing can achieve higher speed. If bearing combined load, angular contact ball bearing should be selected. High precision angular contact ball bearing with special design can achieve very high speed. The rotation speed of thrust bearing is lower than that of radial bearing.